Pressure Sensitive Adhesives: An overview
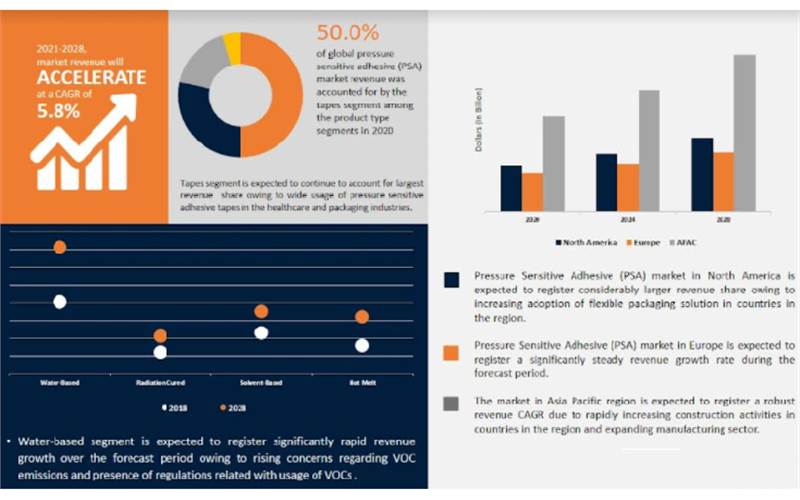
The global Pressure Sensitive Adhesive (PSA) market size was USD 10.19 billion in 2020 and is expected to register a revenue CAGR of 5.8% during the forecast period. Paroma Bhattacharya of Reports and Data shares an overview
29 Sep 2021 | By WhatPackaging? Team
Pressure Sensitive Adhesives (PSAs) are a type of adhesives that are made of a thin, flexible material with a single or double sided coating. Applied to clean and dry surfaces with pressure, pressure sensitive adhesive tapes will adhere to a variety of substrates. To activate pressure sensitive adhesives, no solvent, water, or heat is required. The amount of pressure used to apply the adhesive to the surface has a direct impact on the bond.
PSA tapes are used in a wide range of applications, with new ones being discovered on a nearly daily basis. Because of advancements in adhesive technology, ease of use, and low cost compared to traditional fastening systems, PSA will continue to grow in popularity as a fastening solution.
According to Reports and Data, the global pressure sensitive adhesive (PSA) market size was USD 10.19 billion in 2020 and is expected to register a revenue CAGR of 5.8% during the forecast period.
The benefits of PSA tapes include:
- Materials that are thinner and lighter
- Adheres dissimilar materials together without causing incompatibilities.
- Vibration dampening and noise reduction are provided.
- Cuts assembly time in half
- Surface refinishing is no longer necessary.
- Cosmetically superior by removing visible mechanical fasteners
- Provides a consistent thickness and gap-filling ability.
Pressure-sensitive adhesives are made up of different adhesive components that help to attach or bind things together.
On the basis of materials, pressure-sensitive adhesives are divided into four categories:
- Rubber (natural)
- Rubber that is synthetic
- Acrylic
- Silicone
Based on composition, the global Pressure Sensitive Adhesive (PSA) market has been segmented into acrylic, rubber, ethylene vinyl acetate, silicone, polyurethane, and others.
As per Reports and Data, "The acrylic segment is expected to account for a considerably larger revenue share in the global market owing to good resistance to oxidation and high temperatures and plasticizers. Acrylic based pressure sensitive adhesives were developed to address the aging and environmental limitations of rubber-based tapes. Acrylic pressure sensitive adhesives provide better oxygen and heat resistance in comparison to rubber-based adhesives. The cost effectiveness of acrylic pressure sensitive adhesives as compared to that of silicone-based adhesives is another factor boosting its demand across major industry verticals. PSAs can be used at low temperature and resist weather and moisture and also offer good clarity and color stability. Applications of acrylic pressure sensitive adhesive include decorative trim and outdoor signages, among others. Increasing research and development activities for development and production of modified acrylics that improve dwell time performance, thereby achieving stronger bonds faster, is also expected to drive demand and market growth."
Within each category, there are also distinct adhesives.
Natural Rubber PSAs
Natural rubber (NR) and a tackifying resin are used in natural rubber-based pressure-sensitive adhesives. Their benefits include strong peel strength and good initial adhesion qualities. Natural rubber PSAs can be used for a variety of substrates, both temporary and permanent. Fastening with high green strength that begins with first contact and lower costs, such as support for low-cost backing tapes are other advantages.
However, natural rubber PSAs also have certain drawbacks that include low UV and moisture resistance, a lack of chemical resistance and a high temperature tolerance and oxidation sensitivity.
PSAs made of natural rubber are typically used indoors on low-surface-energy substrates. They are also suitable for applications involving low shear stress on the adhesive.
Synthetic Rubber PSAs
Styrene-butadiene (SBR) or a styrenic block copolymer (SBC) like polystyrene-polyisoprene-polystyrene (SIS) or polystyrene-polybutadiene-polystyrene are used in synthetic rubber-
based pressure sensitive adhesives (SBS). A tackifying resin is also included in these PSAs.
SBR PSAs outperform natural rubber in terms of heat ageing, but they lack the strength, resilience, and low-temperature properties of NR. SBC PSAs are highly adaptable, with the ability to provide aggressive tack or customised peel strength.
Acrylic PSAs
Acrylic pressure-sensitive adhesives are tacky because they are constructed of synthetic resins. Some benefits of acrylic PSAs include excellent oxidation resistance, less expensive
than silicone PSAs, excellent colour consistency and clarity, high-temperature and plasticizer resistance and custom formulations with specific properties.
Acrylic PSAs outperform rubber-based adhesives in terms of heat and oxygen resistance. They are resistant to moisture and weather and can be used at low temperatures. Outdoor signage and decorative trim are examples of applications. Acrylic pressure sensitive adhesives can be used to bridge gaps and link incompatible substrates when applied to thick, high-bond foams (such as metal and glass).
Silicone PSAs
Silicone pressure sensitive adhesives are made of synthetic elastomers that can withstand high temperatures and stick to low-energy surfaces. Their benefits include: chemical resistance, particularly to solvents, moisture, UV, and outgassing resistance, 500°F high-temperature resistance and strength to withstand temperatures as low as -100° F.
Silicone PSAs have one major disadvantage: they are more expensive than other types of pressure-sensitive adhesives. Silicone adhesives are typically used to bond silicone substrates
or silicone-coated materials such as release liners.
Applications of Pressure Sensitive Adhesives:
When used as labels, pressure sensitive adhesives can be divided into the following categories based on adhesion strength: permanent, peelable, ultra-peelable, freezer, and high-
tack.
Permanent adhesives cannot be removed without causing damage to the substrate once they have been placed.
Peelable adhesives can be removed without causing significant damage to the substrate because the adhesive is weaker. But peelable adhesives, on the other hand, might be difficult
to remove because adhesion is still rather strong.
The easiest to remove and leave no residue are ultra-peelable adhesives. They are most commonly used on glass and other substrates where residue is a problem.
Freezer adhesives are made to endure freezing temperatures without impairing the adhesive's performance.
High-tack adhesives are robust and work well on surfaces that are uneven or rough.
The PSA Market
The global Pressure Sensitive Adhesive (PSA) market is moderately fragmented with a number of key players operating on global and regional levels. Major players are engaged in product development and strategic alliances to expand their respective product portfolios and gain a robust footing in the global market.
Some key players in the market include Henkel AG & Co. KGaA, The Dow Chemical Company, Avery Dennison Corporation, HB Fuller Company, The 3M Company, Arkema SA, Sika AG, Scapa Group, Ashland Global Specialty Chemicals Inc., and Franklin Adhesives & Polymers.
The global pressure sensitive adhesive (PSA) market size is expected to reach USD 15.98 Billion in 2028 and register a revenue CAGR of 5.8% over the forecast period, according to the latest report by Reports and Data. Steady growth in the construction industry and increasing number of construction activities in developing countries are some key factors expected to drive market revenue growth during the forecast period.
The construction industry is increasingly utilising pressure sensitive adhesive as an insulation barrier around doors and windows. Pressure sensitive adhesives prevent water and air from infiltrating the home, which enables enhancing energy efficiency as well as longevity and durability of buildings. Advancements in design of customer electronics is projected to boost demand for PSAs and drive revenue growth of the market during the forecast period. Increasing demand for electronic devices that are continually decreasing in size and increasing in efficiency and functionality are driving rapid demand for pressure sensitive adhesives.










 See All
See All